[ Back to main ]
[ Back to colors page ]
Color to Gray Conversion
About
Occasionally the need arises to convert an RGB color image to
grayscale. Until I faced this problem, I naively thought it a
trivial conversion. It is not at all. My goal was to collect all
the isoluminant colors from the RGB color space for every level
of gray which is practically a gray conversion of all RGB colors
and a second step grading. I wanted to map the closest and least
distinguishable gray value to every RGB color. I explored many
of the existing methods, I examined the results of many popular
softwares, and got a headache. Would you imagine, that almost
all Photoshop versions does this conversion differently from the
others? At least, Photoshop does a decent job, which is not the
case with some other softwares. Despite GIMP 2.10 won this test
for me, I ended up using with my own method which is based again
on the Delta-E 2000 (dE2000) formula. My results are very close
to the GIMP's and they fit better to the line of my research.
Existing Methods
Average of the Channels
An intuitive way to convert a three component RGB color value to
a single gray value is to take the average of the red, green,
and blue values to get the grayscale value. This combines the
luminance contributed by each color band into a reasonable gray
approximation. However, to our eyes, green looks about ten times
brighter than blue.
Weighted Average of the Channels
There is no consensus about the weights. According to a source,
Photoshop uses 30% red, 59% green and 11% blue. The ITU-R BT.601
standard uses 0.299 red, 0.587 green, and 0.114 blue ratios.
Relative Luminance After Linearization
Scientists have figured out how different we perceive the lumi-
nance or red, green, and blue. The ITU recommends the following
commonly used formula for the HDTV standards:
Y = 0.2126 * R_lin + 0.7152 * G_lin + 0.0722 * B_lin
However, the RGB values should be linearized first. For that, we
divide the values by 255 to convert them to the range of 0 to 1.
Then, linearization. A simple method is to power the values with
2.2 exponent. You can find the more complicated standard method
here. Finally, gamma correction, multiplication by 255, round to
integer has to be applied on the Y value to get our gray value.
Other Methods
There are a plenty of other methods available. You can see many
of them here and here.
My Method
Taking the huge variety and inconsitency of the methods, I made
my own one, which fits better to my experiment than any other I
found. As my whole color palette project is based on the CIELAB
Delta-E 2000 formula, soon it came obvious to me that I should
continue using that for this part of the project too. Thus, for
every RGB value I mapped the R=G=B gray value with the lowest
delta-E value. I stored the mapping in a lossless 4096x4096 Hald
CLUT. Later I found that the result is not fully monotonic. None
of the differences were more than 1 gray value in the range of 0
to 255. I fixed the monotonicity of the LUT anyway.
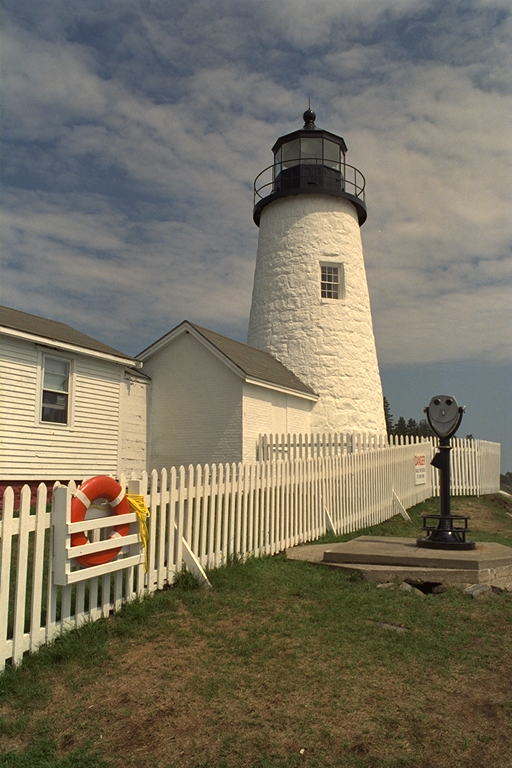
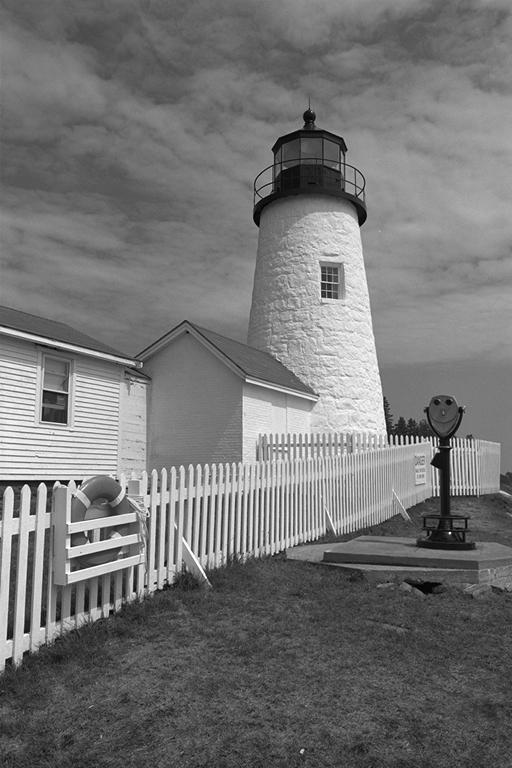


 Visual Comparision
I collected many conversion methods in the form of Hald CLUTs.
Basically I applied the methods on the identity CLUT and saved
the results. I also created a comparision image with Python to
see them all together. The best conversion methods are the ones
where the readability of the text is the worst over the entire
column. Personally I found GIMP 2.10 the best one. Photoshop is
also good, except for version 21 (PS 2020). The one tagged with
"lp" refers to the lodgepole Python module by Brandon Rohrer. My
own methods are "de2000" and "szieberth" (monotonic). Despite I
visually find GIMP better by half a hair, I picked my own method
for the next steps of my project for consistency.
Usage
With the Hald CLUTs provided, you can easily apply any grayscale
conversion to your images with the command prompt if ImageMagick
is installed. Use the following command:
magick inputimage.png haldclut.png -hald-clut outputimage.png
You can find the GRAYSCALE and CVD palette projects on GitHub.
Visual Comparision
I collected many conversion methods in the form of Hald CLUTs.
Basically I applied the methods on the identity CLUT and saved
the results. I also created a comparision image with Python to
see them all together. The best conversion methods are the ones
where the readability of the text is the worst over the entire
column. Personally I found GIMP 2.10 the best one. Photoshop is
also good, except for version 21 (PS 2020). The one tagged with
"lp" refers to the lodgepole Python module by Brandon Rohrer. My
own methods are "de2000" and "szieberth" (monotonic). Despite I
visually find GIMP better by half a hair, I picked my own method
for the next steps of my project for consistency.
Usage
With the Hald CLUTs provided, you can easily apply any grayscale
conversion to your images with the command prompt if ImageMagick
is installed. Use the following command:
magick inputimage.png haldclut.png -hald-clut outputimage.png
You can find the GRAYSCALE and CVD palette projects on GitHub.


 Visual Comparision
I collected many conversion methods in the form of Hald CLUTs.
Basically I applied the methods on the identity CLUT and saved
the results. I also created a comparision image with Python to
see them all together. The best conversion methods are the ones
where the readability of the text is the worst over the entire
column. Personally I found GIMP 2.10 the best one. Photoshop is
also good, except for version 21 (PS 2020). The one tagged with
"lp" refers to the lodgepole Python module by Brandon Rohrer. My
own methods are "de2000" and "szieberth" (monotonic). Despite I
visually find GIMP better by half a hair, I picked my own method
for the next steps of my project for consistency.
Usage
With the Hald CLUTs provided, you can easily apply any grayscale
conversion to your images with the command prompt if ImageMagick
is installed. Use the following command:
magick inputimage.png haldclut.png -hald-clut outputimage.png
You can find the GRAYSCALE and CVD palette projects on GitHub.
Visual Comparision
I collected many conversion methods in the form of Hald CLUTs.
Basically I applied the methods on the identity CLUT and saved
the results. I also created a comparision image with Python to
see them all together. The best conversion methods are the ones
where the readability of the text is the worst over the entire
column. Personally I found GIMP 2.10 the best one. Photoshop is
also good, except for version 21 (PS 2020). The one tagged with
"lp" refers to the lodgepole Python module by Brandon Rohrer. My
own methods are "de2000" and "szieberth" (monotonic). Despite I
visually find GIMP better by half a hair, I picked my own method
for the next steps of my project for consistency.
Usage
With the Hald CLUTs provided, you can easily apply any grayscale
conversion to your images with the command prompt if ImageMagick
is installed. Use the following command:
magick inputimage.png haldclut.png -hald-clut outputimage.png
You can find the GRAYSCALE and CVD palette projects on GitHub.